Cloud providers have revolutionized how businesses deploy and scale their applications. This guide will help you understand the major cloud platforms and their impact on modern technology.
What You’ll Learn
- What are cloud providers and their history?
- Key use cases for cloud computing
- Current cloud adoption rates and trends
- Comparison of major cloud providers
- How to choose the right cloud platform
- Learning resources for cloud computing
Understanding Cloud Providers
Cloud providers have taken the tech world by storm. Amazon led the way with cloud computing in 2006 when it launched Amazon EC2. The cloud, however, was mentioned as early as 1998.
The Flexera state of the cloud report provides a snapshot of cloud computing. The Flexera report is compiled annually and describes how companies use cloud providers and their adoption rates.
Primary Use Cases
Companies use cloud providers for innumerable reasons. There are many use cases due to the flexibility, and interoperability cloud services provide.
Here are the primary use cases.
- Hosting servers on virtual machines and containers
- Running serverless workloads
- Solving large-scale computing problems like big data analysis, machine learning, and artificial intelligence
Cloud Adoption Trends
Cloud providers have multiplied to service widespread digital transformations. Cloud adoption is mixed between public and private clouds.
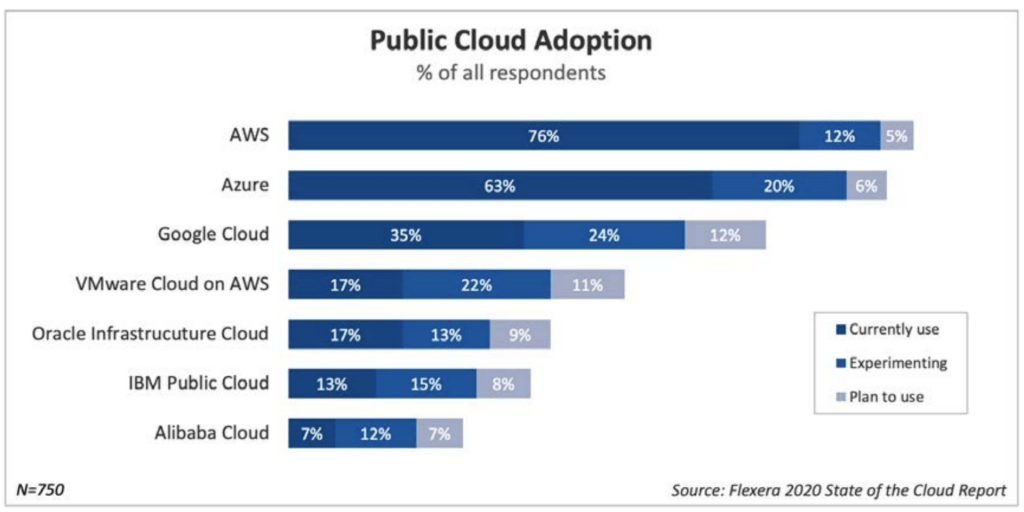
Public Cloud Adoption
Amazon Web Services leads the pack, while Microsoft Azure is slightly behind. Google has a share but started later and has fewer relationships with large enterprises.
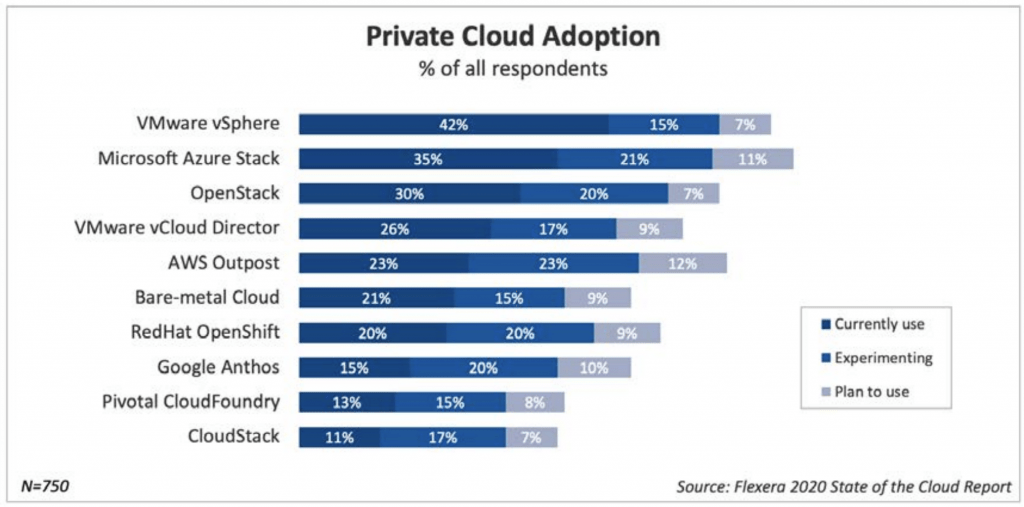
Private Cloud Adoption
Private clouds are an alternative to public clouds. They reduce the complexity of resource hosting by providing accessible APIs.
Major Cloud Providers
Amazon Web Services (AWS)

In 2002 the AWS platform was born. This emergence was a classic case of dogfooding since Amazon needed web-scale services. Why wouldn’t Amazon attempt to recoup some of its hosting costs by reselling its platforms?
The AWS platform applies the single-responsibility principle to its services in most cases. Services like LightSail aggregate services into a single service.
Microsoft Azure

Microsoft Azure is like AWS in many ways. It provides scalable services that complement its business productivity solutions. Azure’s cloud services appear like a monolith within the Azure Web Portal. Under the hood, single-responsibility services like Azure Functions allow you to run functions in the cloud.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)

Google’s services have evolved in fits over the years. Google App Engine was released in 2008 and only ran Python applications. Now Google App Engine supports many languages. Google’s cloud services resemble other cloud services, as evidenced by the Google Cloud Functions service.
Other Cloud Providers
I could go on and on like Larry Ellison, but I’ll spare you. Luckily, the software industry is a shining bastion of commerce. It is booming, and competition is fierce. There’s plenty of room for Oracle, VMWare, Red Hat, and others.
Future of Cloud Computing
Cloud providers are continually evolving. Trends come and go, and the war rages on between cloud-native vs. containers. Software developers are winning the cloud computing wars. If software developers can keep choice overload at bay, they will continue to benefit from cloud providers.
Learning Resources
Recommended Books
- Digital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass Extinction - Amazon
- A Brief Guide to Cloud Computing - Amazon
Online Courses
- Fundamentals of Cloud Computing - Pluralsight
- Cloud Computing: The Big Picture - Pluralsight
- Learning Cloud Computing: Core Concepts - LinkedIn
- Cloud Computing Concepts - Udemy

Comments #